Harvard’s half-billion land stake in Brazil marred by conflict and abuse
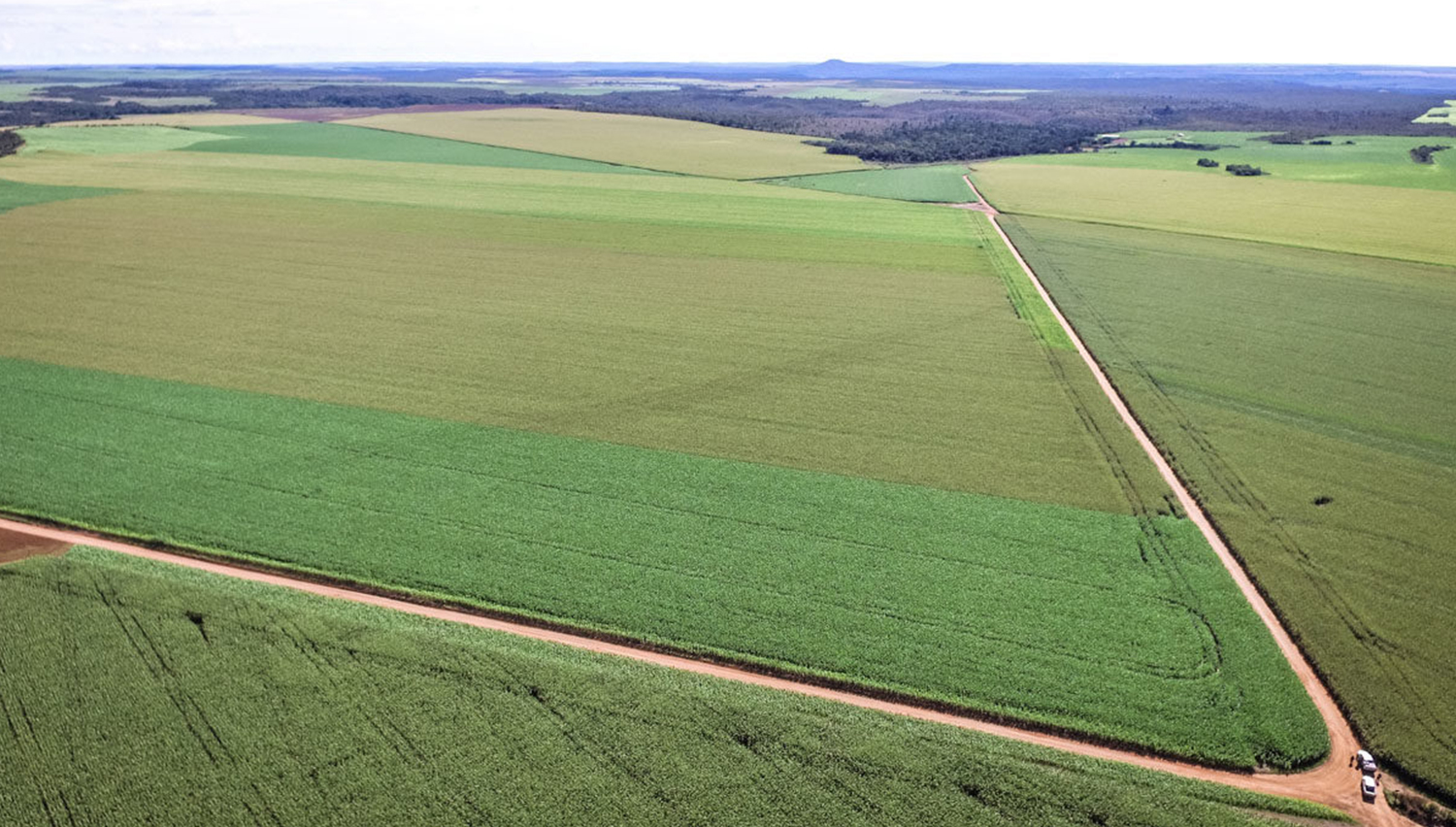

- Harvard University has plowed $450 million of its $40 billion endowment in Brazil, most of it to buying up at least 405,000 hectares (1 million acres) of land in the Cerrado.
- This is a region where major landowners have racked up human rights violations against smallholder farmers and crimes against the environment.
- Most investments in land in this region are purely speculative; while the land goes unused, locals are deprived of their water sources, farmland and other resources.
- Harvard would not comment on its Brazilian investments specifically, but said it is trying to divest from unsustainable ventures. But even as it has trouble finding buyers for the farms, it continues to profit from the appreciating value of the land.
After the 2008 economic crisis, Harvard University, one of the most respected educational institutions in the world, sought to reallocate its endowment funds to safer assets. It invested more than $1 billion in land in Brazil, Africa, Oceania, Eastern Europe and the United States.
But a recent report shows that in Brazil, which accounts for almost half of Harvard’s total investment, at $450 million, most of the endowment’s acquired enterprises are territories occupied by land-grabbers in conflict with traditional communities and slave-descended quilombos in the Cerrado grasslands. The report, by GRAIN, a nonprofit that advocates for small farmers, and Rede Social de Justiça e Direitos Humanos, a social justice NGO, also links these lands to incidents of deforestation and death threats.
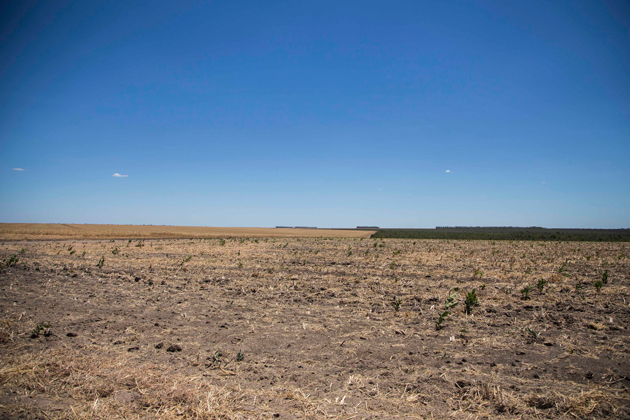
Most of the properties are speculative investments; the land, even when unproductive, is considered a safe investment in times of crisis or otherwise. To date, the university’s efforts to divest from these enterprises have been unsuccessful.
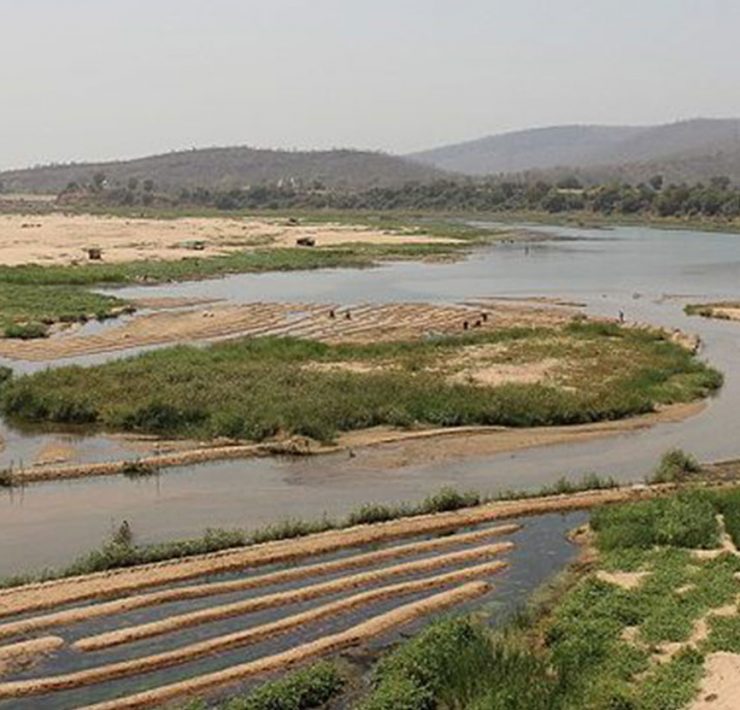
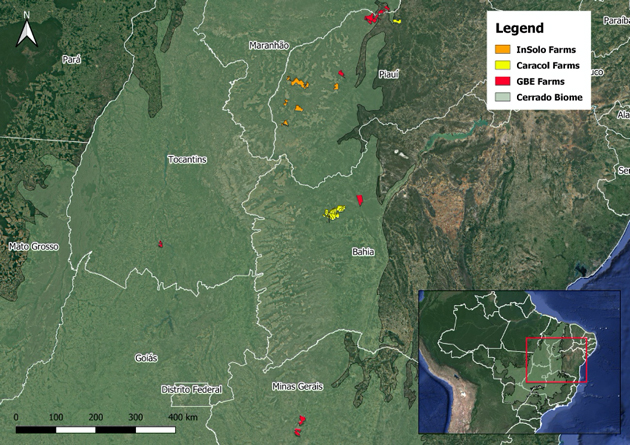
It owns a total of 405,000 hectares (1 million acres) — nearly 5,000 times the size of the Harvard campus in Cambridge, Massachusetts — spread across about 40 farms. Most are located in the states of Maranhão, Tocantins, Piauí and Bahia, in the zone of the Cerrado known as Matopiba. It’s a region dominated by agribusiness and that has, in recent years, seen extreme levels of illegal deforestation and rural violence.
When contacted by Mongabay, Harvard University’s press office stated it “does not comment on specific investments.”
Land as financial asset
In October 2019, Altamiran Lopes Ribeiro, who works with the Catholic Church-affiliated Pastoral Land Commission (CPT) in Piauí, went to Harvard to talk about the reality of the communities in which he operates and which are now impacted by foreign enterprises. He also wanted to hear what students and faculty had to say.
Most of the people he met at the university were unaware of how their money was being invested, Ribeiro says. “Our idea was to sensitize these people to the reality. To show them what goes on so that they can pressure the managers to withdraw their money from these enterprises.” In 2019, the CPT recorded 376 land conflicts in the four states of Matopiba.
Though the university has not acquired any land recently, Harvard representatives have also been unable to sell off the troubled farms. Yet despite the difficulty finding buyers, the university continues to profit from its holdings, with the land appreciating in value.
“Their intention is not to produce anything. It’s to have the land as a financial asset,” Ribeiro says. Since Brazilian law prohibits foreigners from directly purchasing land, Harvard’s endowment and others of its kind use shell companies. “And then they buy from land-grabbers, whoever they may be. They earn money on the stock exchange, they earn by renting, producing or letting the land appreciate. It’s a safer investment than others,” Ribeiro says.
Sinking hundreds of millions of dollars into lands “conquered in exchange for blood,” as Ribeiro puts it, is a risky business. But it’s also profitable when taking into account the amnesty provided by states and the federal government to deforesters and land grabbers through state laws, provisional measures, and bills currently circulating in Congress.

Policy that favors criminals
Not even the pandemic, which has led to more than 109,000 deaths in Brazil, has slowed what critics say is the federal government’s impetus to legalize land theft — in other words, the process of land-grabbing. This type of amnesty favors all kinds of illegal operations, and foreign funds also benefit from it.
Brazilian Environment Minister Ricardo Salles called COVID-19 an opportunity “to move in the cattle,” and the Bolsonaro administration has rushed to undo environmental protections for the benefit of agribusiness and large investors.
The so-called provisional measure for land-grabbing is now Bill 2633/20, and it could be voted on in Congress at any time. Criticized in detail by various organizations, such as the Socioenvironmental Institute (ISA) and Imazon, a conservation nonprofit, the bill may provide amnesty for the irregular appropriation of millions of hectares, heighten conflicts, cause an even greater concentration of land in the hands of the few, and drive further deforestation. Changes in the Terra Legal program under the administration of former president Michel Temer already represent a huge gain for criminals.

In Matopiba, state laws already passed or currently being discussed follow the same path. The threat is real, says Larissa Packer of GRAIN. “They are giving amnesty for invasions into public lands, which are then sold at a discount of up to 90% on the prices set by INCRA [the federal land reform agency] 20 years ago. In other words: for free,” Packer says. All this makes the land market in Brazil, as risky as it may seem, very profitable.
According to Packer, the Harvard endowment is “desperate to sell its rotten securities that have large environmental liabilities and are facing lawsuits,” and that includes the lands it owns in Brazil. But if the land is formally regularized by these bills, “then it’s over, the conflict is erased.” The report shows that Harvard has always been aware of the local problems.
In a statement sent by the Harvard Management Company’s press office, the endowment is in general trying to “reposition its portfolio” of natural resources all over the world. Investments deemed unsustainable were reduced from 9% to 4% of the total in the last three years, beginning with the hiring of new a management team that inherited “deeply problematic assets.”
According to the press office, Harvard has already gotten rid of more than $1 billion in such investments, and this year is attempting to sell another $200 million of projects considered “good, but not in compliance” with its current guidelines on sustainable investing.
Daniela Stefano, from Rede Social de Justiça e Direitos Humanos, visited communities in Piauí and Bahia affected by Harvard’s enterprises. The local reality, she says, includes death threats, the presence of armed guards, arbitrarily built fences, the massive use of pesticides, and the co-opting of local leaders.
Between the cities of Jerumenha and Floriano, in Piauí, the quilombola community of Arthur Passos has experienced real devastation with the arrival of Terracal, the local company representing Harvard. “The lands, kept unproductive, are surrounded by fences and kept under surveillance,” Stefano says. As they lie close to the river, these are the same lands that people used for everything: planting, fishing, raising small animals, and growing fruits and medicinal plants. “Today the community is divided and is in danger of losing its title as a traditional quilombola community,” Stefano says.

This article first appeared on Mongabay.